In PHP 5 there are some new functions. Here is the list of them:
Arrays:
array_combine() - Creates an array by using one array for keys and another for its values
array_diff_uassoc() - Computes the difference of arrays with additional index check which is performed by a user supplied callback function
array_udiff() - Computes the difference of arrays by using a callback function for data comparison
array_udiff_assoc() - Computes the difference of arrays with additional index check. The data is compared by using a callback function
array_udiff_uassoc() - Computes the difference of arrays with additional index check. The data is compared by using a callback function. The index check is done by a callback function also
array_walk_recursive() - Apply a user function recursively to every member of an array
array_uintersect_assoc() - Computes the intersection of arrays with additional index check. The data is compared by using a callback function
array_uintersect_uassoc() - Computes the intersection of arrays with additional index check. Both the data and the indexes are compared by using separate callback functions
array_uintersect() - Computes the intersection of arrays. The data is compared by using a callback function
InterBase:
ibase_affected_rows() - Return the number of rows that were affected by the previous query
ibase_backup() - Initiates a backup task in the service manager and returns immediately
ibase_commit_ret() - Commit a transaction without closing it
ibase_db_info() - Request statistics about a database
ibase_drop_db() - Drops a database
ibase_errcode() - Return an error code
ibase_free_event_handler() - Cancels a registered event handler
ibase_gen_id() - Increments the named generator and returns its new value
ibase_maintain_db() - Execute a maintenance command on the database server
ibase_name_result() - Assigns a name to a result set
ibase_num_params() - Return the number of parameters in a prepared query
ibase_param_info() - Return information about a parameter in a prepared query
ibase_restore() - Initiates a restore task in the service manager and returns immediately
ibase_rollback_ret() - Rollback transaction and retain the transaction context
ibase_server_info() - Request statistics about a database server
ibase_service_attach() - Connect to the service manager
ibase_service_detach() - Disconnect from the service manager
ibase_set_event_handler() - Register a callback function to be called when events are posted
ibase_wait_event() - Wait for an event to be posted by the database
iconv:
iconv_mime_decode() - Decodes a MIME header field
iconv_mime_decode_headers() - Decodes multiple MIME header fields at once
iconv_mime_encode() - Composes a MIME header field
iconv_strlen() - Returns the character count of string
iconv_strpos() - Finds position of first occurrence of a needle within a haystack
iconv_strrpos() - Finds the last occurrence of a needle within a haystack
iconv_substr() - Cut out part of a string
Streams:
stream_copy_to_stream() - Copies data from one stream to another
stream_get_line() - Gets line from stream resource up to a given delimiter
stream_socket_accept() - Accept a connection on a socket created by stream_socket_server()
stream_socket_client() - Open Internet or Unix domain socket connection
stream_socket_get_name() - Retrieve the name of the local or remote sockets
stream_socket_recvfrom() - Receives data from a socket, connected or not
stream_socket_sendto() - Sends a message to a socket, whether it is connected or not
stream_socket_server() - Create an Internet or Unix domain server socket
Date and time related:
idate() - Format a local time/date as integer
date_sunset() - Time of sunset for a given day and location
date_sunrise() - Time of sunrise for a given day and location
time_nanosleep() - Delay for a number of seconds and nanoseconds
Strings:
str_split() - Convert a string to an array
strpbrk() - Search a string for any of a set of characters
substr_compare() - Binary safe optionally case insensitive comparison of two strings from an offset, up to length characters
Other:
convert_uudecode() - decode a uuencoded string
convert_uuencode() - uuencode a string
curl_copy_handle() - Copy a cURL handle along with all of its preferences
dba_key_split() - Splits a key in string representation into array representation
dbase_get_header_info() - Get the header info of a dBase database
dbx_fetch_row() - Fetches rows from a query-result that had the DBX_RESULT_UNBUFFERED flag set
fbsql_set_password() - Change the password for a given user
file_put_contents() - Write a string to a file
ftp_alloc() - Allocates space for a file to be uploaded
get_declared_interfaces() - Returns an array of all declared interfaces
get_headers() - Fetches all the headers sent by the server in response to a HTTP request
headers_list() - Returns a list of response headers sent (or ready to send)
http_build_query() - Generate URL-encoded query string
image_type_to_extension() - Get file extension for image-type returned by getimagesize(), exif_read_data(), exif_thumbnail(), exif_imagetype()
imagefilter() - Applies a filter to an image using custom arguments
imap_getacl() - Gets the ACL for a given mailbox
ldap_sasl_bind() - Bind to LDAP directory using SASL
mb_list_encodings() - Returns an array of all supported encodings
pcntl_getpriority() - Get the priority of any process
pcntl_wait() - Waits on or returns the status of a forked child as defined by the waitpid() system call
pg_version() - Returns an array with client, protocol and server version (when available)
php_check_syntax() - Check the syntax of the specified file
php_strip_whitespace() - Return source with stripped comments and whitespace
proc_nice() - Change the priority of the current process
pspell_config_data_dir() - Change location of language data files
pspell_config_dict_dir() - Change location of the main word list
setrawcookie() - Send a cookie without URL-encoding the value
scandir() - List files and directories inside the specified path
snmp_read_mib() - Reads and parses a MIB file into the active MIB tree
sqlite_fetch_column_types() - Return an array of column types from a particular table
CodeIgniter is an Application Development Framework - a toolkit - for people who build web sites using PHP. Its goal is to enable you to develop projects much faster than you could if you were writing code from scratch, by providing a rich set of libraries for commonly needed tasks, as well as a simple interface and logical structure to access these libraries. CodeIgniter lets you creatively focus on your project by minimizing the amount of code needed for a given task.
Monday, 11 July 2011
AJAX :: POLL Example
AJAX Poll
The following example will demonstrate a poll where the result is shown without reloading.Do you like PHP and AJAX so far?
Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user choose an option above, a function called "getVote()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onclick" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function getVote(int) { if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("poll").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","poll_vote.php?vote="+int,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <div id="poll"> <h3>Do you like PHP and AJAX so far?</h3> <form> Yes: <input type="radio" name="vote" value="0" onclick="getVote(this.value)" /> <br />No: <input type="radio" name="vote" value="1" onclick="getVote(this.value)" /> </form> </div> </body> </html> |
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (vote) is added to the URL (with the value of the yes or no option)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "poll_vote.php":| <?php $vote = $_REQUEST['vote']; //get content of textfile $filename = "poll_result.txt"; $content = file($filename); //put content in array $array = explode("||", $content[0]); $yes = $array[0]; $no = $array[1]; if ($vote == 0) { $yes = $yes + 1; } if ($vote == 1) { $no = $no + 1; } //insert votes to txt file $insertvote = $yes."||".$no; $fp = fopen($filename,"w"); fputs($fp,$insertvote); fclose($fp); ?> <h2>Result:</h2> <table> <tr> <td>Yes:</td> <td> <img src="poll.gif" width='<?php echo(100*round($yes/($no+$yes),2)); ?>' height='20'> <?php echo(100*round($yes/($no+$yes),2)); ?>% </td> </tr> <tr> <td>No:</td> <td> <img src="poll.gif" width='<?php echo(100*round($no/($no+$yes),2)); ?>' height='20'> <?php echo(100*round($no/($no+$yes),2)); ?>% </td> </tr> </table> |
- Get the content of the "poll_result.txt" file
- Put the content of the file in variables and add one to the selected variable
- Write the result to the "poll_result.txt" file
- Output a graphical representation of the poll result
The Text File
The text file (poll_result.txt) is where we store the data from the poll.It is stored like this:
| 0||0 |
Note: Remember to allow your web server to edit the text file. Do NOT give everyone access, just the web server (PHP).
AJAX :: RSS Reader
An RSS Reader is used to read RSS Feeds.
AJAX RSS Reader
The following example will demonstrate an RSS reader, where the RSS-feed is loaded into a webpage without reloading:Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user selects an RSS-feed in the dropdown list above, a function called "showResult()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onchange" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function showRSS(str) { if (str.length==0) { document.getElementById("rssOutput").innerHTML=""; return; } if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("rssOutput").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","getrss.php?q="+str,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <form> <select onchange="showRSS(this.value)"> <option value="">Select an RSS-feed:</option> <option value="Google">Google News</option> <option value="MSNBC">MSNBC News</option> </select> </form> <br /> <div id="rssOutput">RSS-feed will be listed here...</div> </body> </html> |
- Check if an RSS-feed is selected
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (q) is added to the URL (with the content of the dropdown list)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "getrss.php":| <?php //get the q parameter from URL $q=$_GET["q"]; //find out which feed was selected if($q=="Google") { $xml=("http://news.google.com/news?ned=us&topic=h&output=rss"); } elseif($q=="MSNBC") { $xml=("http://rss.msnbc.msn.com/id/3032091/device/rss/rss.xml"); } $xmlDoc = new DOMDocument(); $xmlDoc->load($xml); //get elements from "<channel>" $channel=$xmlDoc->getElementsByTagName('channel')->item(0); $channel_title = $channel->getElementsByTagName('title') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; $channel_link = $channel->getElementsByTagName('link') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; $channel_desc = $channel->getElementsByTagName('description') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; //output elements from "<channel>" echo("<p><a href='" . $channel_link . "'>" . $channel_title . "</a>"); echo("<br />"); echo($channel_desc . "</p>"); //get and output "<item>" elements $x=$xmlDoc->getElementsByTagName('item'); for ($i=0; $i<=2; $i++) { $item_title=$x->item($i)->getElementsByTagName('title') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; $item_link=$x->item($i)->getElementsByTagName('link') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; $item_desc=$x->item($i)->getElementsByTagName('description') ->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue; echo ("<p><a href='" . $item_link . "'>" . $item_title . "</a>"); echo ("<br />"); echo ($item_desc . "</p>"); } ?> |
- Check which feed was selected
- Create a new XML DOM object
- Load the RSS document in the xml variable
- Extract and output elements from the channel element
- Extract and output elements from the item element
AJAX :: Live Search
AJAX can be used to create more user-friendly and interactive searches.
AJAX Live Search
The following example will demonstrate a live search, where you get search results while you type.Live search has many benefits compared to traditional searching:
- Results are shown as you type
- Results narrow as you continue typing
- If results become too narrow, remove characters to see a broader result
The results in the example above are found in an XML file (links.xml). To make this example small and simple, only eight results are available.
Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user types a character in the input field above, the function "showResult()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onkeyup" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function showResult(str) { if (str.length==0) { document.getElementById("livesearch").innerHTML=""; document.getElementById("livesearch").style.border="0px"; return; } if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("livesearch").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; document.getElementById("livesearch").style.border="1px solid #A5ACB2"; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","livesearch.php?q="+str,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <form> <input type="text" size="30" onkeyup="showResult(this.value)" /> <div id="livesearch"></div> </form> </body> </html> |
If the input field is empty (str.length==0), the function clears the content of the livesearch placeholder and exits the function.
If the input field is not empty, the showResult() function executes the following:
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (q) is added to the URL (with the content of the input field)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "livesearch.php".The source code in "livesearch.php" searches an XML file for titles matching the search string and returns the result:
| <?php $xmlDoc=new DOMDocument(); $xmlDoc->load("links.xml"); $x=$xmlDoc->getElementsByTagName('link'); //get the q parameter from URL $q=$_GET["q"]; //lookup all links from the xml file if length of q>0 if (strlen($q)>0) { $hint=""; for($i=0; $i<($x->length); $i++) { $y=$x->item($i)->getElementsByTagName('title'); $z=$x->item($i)->getElementsByTagName('url'); if ($y->item(0)->nodeType==1) { //find a link matching the search text if (stristr($y->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue,$q)) { if ($hint=="") { $hint="<a href='" . $z->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue . "' target='_blank'>" . $y->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue . "</a>"; } else { $hint=$hint . "<br /><a href='" . $z->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue . "' target='_blank'>" . $y->item(0)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue . "</a>"; } } } } } // Set output to "no suggestion" if no hint were found // or to the correct values if ($hint=="") { $response="no suggestion"; } else { $response=$hint; } //output the response echo $response; ?> |
- Load an XML file into a new XML DOM object
- Loop through all <title> elements to find matches from the text sent from the JavaScript
- Sets the correct url and title in the "$response" variable. If more than one match is found, all matches are added to the variable
- If no matches are found, the $response variable is set to "no suggestion"
Labels:
DOMDocument,
Live Search,
PHP,
XML,
XML DOM,
XMLHttpRequest
AJAX :: XML and AJAX
AJAX can be used for interactive communication with an XML file.
AJAX XML Example
The following example will demonstrate how a web page can fetch information from an XML file with AJAX:Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user selects a CD in the dropdown list above, a function called "showCD()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onchange" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function showCD(str) { if (str=="") { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=""; return; } if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","getcd.php?q="+str,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <form> Select a CD: <select name="cds" onchange="showCD(this.value)"> <option value="">Select a CD:</option> <option value="Bob Dylan">Bob Dylan</option> <option value="Bonnie Tyler">Bonnie Tyler</option> <option value="Dolly Parton">Dolly Parton</option> </select> </form> <div id="txtHint"><b>CD info will be listed here...</b></div> </body> </html> |
- Check if a CD is selected
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (q) is added to the URL (with the content of the dropdown list)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "getcd.php".The PHP script loads an XML document, "cd_catalog.xml", runs a query against the XML file, and returns the result as HTML:
| <?php $q=$_GET["q"]; $xmlDoc = new DOMDocument(); $xmlDoc->load("cd_catalog.xml"); $x=$xmlDoc->getElementsByTagName('ARTIST'); for ($i=0; $i<=$x->length-1; $i++) { //Process only element nodes if ($x->item($i)->nodeType==1) { if ($x->item($i)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue == $q) { $y=($x->item($i)->parentNode); } } } $cd=($y->childNodes); for ($i=0;$i<$cd->length;$i++) { //Process only element nodes if ($cd->item($i)->nodeType==1) { echo("<b>" . $cd->item($i)->nodeName . ":</b> "); echo($cd->item($i)->childNodes->item(0)->nodeValue); echo("<br />"); } } ?> |
- PHP creates an XML DOM object
- Find all <artist> elements that matches the name sent from the JavaScript
- Output the album information (send to the "txtHint" placeholder)
AJAX can be used for interactive communication with a database.
AJAX Database Example
The following example will demonstrate how a web page can fetch information from a database with AJAX:Example Explained - The MySQL Database
The database table we use in the example above looks like this:| id | FirstName | LastName | Age | Hometown | Job |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Peter | Griffin | 41 | Quahog | Brewery |
| 2 | Lois | Griffin | 40 | Newport | Piano Teacher |
| 3 | Joseph | Swanson | 39 | Quahog | Police Officer |
| 4 | Glenn | Quagmire | 41 | Quahog | Pilot |
Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user selects a user in the dropdown list above, a function called "showUser()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onchange" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function showUser(str) { if (str=="") { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=""; return; } if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","getuser.php?q="+str,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <form> <select name="users" onchange="showUser(this.value)"> <option value="">Select a person:</option> <option value="1">Peter Griffin</option> <option value="2">Lois Griffin</option> <option value="3">Glenn Quagmire</option> <option value="4">Joseph Swanson</option> </select> </form> <br /> <div id="txtHint"><b>Person info will be listed here.</b></div> </body> </html> |
- Check if a person is selected
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (q) is added to the URL (with the content of the dropdown list)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "getuser.php".The source code in "getuser.php" runs a query against a MySQL database, and returns the result in an HTML table:
| <?php $q=$_GET["q"]; $con = mysql_connect('localhost', 'peter', 'abc123'); if (!$con) { die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error()); } mysql_select_db("ajax_demo", $con); $sql="SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = '".$q."'"; $result = mysql_query($sql); echo "<table border='1'> <tr> <th>Firstname</th> <th>Lastname</th> <th>Age</th> <th>Hometown</th> <th>Job</th> </tr>"; while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)) { echo "<tr>"; echo "<td>" . $row['FirstName'] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row['LastName'] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row['Age'] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row['Hometown'] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row['Job'] . "</td>"; echo "</tr>"; } echo "</table>"; mysql_close($con); ?> |
- PHP opens a connection to a MySQL server
- The correct person is found
- An HTML table is created, filled with data, and sent back to the "txtHint" placeholder
AJAX :: PHP
AJAX PHP Example
The following example will demonstrate how a web page can communicate with a web server while a user type characters in an input field:Example Explained - The HTML Page
When a user types a character in the input field above, the function "showHint()" is executed. The function is triggered by the "onkeyup" event:| <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function showHint(str) { if (str.length==0) { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=""; return; } if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { document.getElementById("txtHint").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText; } } xmlhttp.open("GET","gethint.php?q="+str,true); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <p><b>Start typing a name in the input field below:</b></p> <form> First name: <input type="text" onkeyup="showHint(this.value)" size="20" /> </form> <p>Suggestions: <span id="txtHint"></span></p> </body> </html> |
If the input field is empty (str.length==0), the function clears the content of the txtHint placeholder and exits the function.
If the input field is not empty, the showHint() function executes the following:
- Create an XMLHttpRequest object
- Create the function to be executed when the server response is ready
- Send the request off to a file on the server
- Notice that a parameter (q) is added to the URL (with the content of the input field)
The PHP File
The page on the server called by the JavaScript above is a PHP file called "gethint.php".The source code in "gethint.php" checks an array of names, and returns the corresponding name(s) to the browser:
| <?php // Fill up array with names $a[]="Anna"; $a[]="Brittany"; $a[]="Cinderella"; $a[]="Diana"; $a[]="Eva"; $a[]="Fiona"; $a[]="Gunda"; $a[]="Hege"; $a[]="Inga"; $a[]="Johanna"; $a[]="Kitty"; $a[]="Linda"; $a[]="Nina"; $a[]="Ophelia"; $a[]="Petunia"; $a[]="Amanda"; $a[]="Raquel"; $a[]="Cindy"; $a[]="Doris"; $a[]="Eve"; $a[]="Evita"; $a[]="Sunniva"; $a[]="Tove"; $a[]="Unni"; $a[]="Violet"; $a[]="Liza"; $a[]="Elizabeth"; $a[]="Ellen"; $a[]="Wenche"; $a[]="Vicky"; //get the q parameter from URL $q=$_GET["q"]; //lookup all hints from array if length of q>0 if (strlen($q) > 0) { $hint=""; for($i=0; $i<count($a); $i++) { if (strtolower($q)==strtolower(substr($a[$i],0,strlen($q)))) { if ($hint=="") { $hint=$a[$i]; } else { $hint=$hint." , ".$a[$i]; } } } } // Set output to "no suggestion" if no hint were found // or to the correct values if ($hint == "") { $response="no suggestion"; } else { $response=$hint; } //output the response echo $response; ?> |
- Find a name matching the characters sent from the JavaScript
- If no match were found, set the response string to "no suggestion"
- If one or more matching names were found, set the response string to all these names
- The response is sent to the "txtHint" placeholder
AJAX :: introduction
AJAX is about updating parts of a web page, without reloading the whole page.
What is AJAX?
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.AJAX is a technique for creating fast and dynamic web pages.
AJAX allows web pages to be updated asynchronously by exchanging small amounts of data with the server behind the scenes. This means that it is possible to update parts of a web page, without reloading the whole page.
Classic web pages, (which do not use AJAX) must reload the entire page if the content should change.
Examples of applications using AJAX: Google Maps, Gmail, Youtube, and Facebook tabs.
How AJAX Works
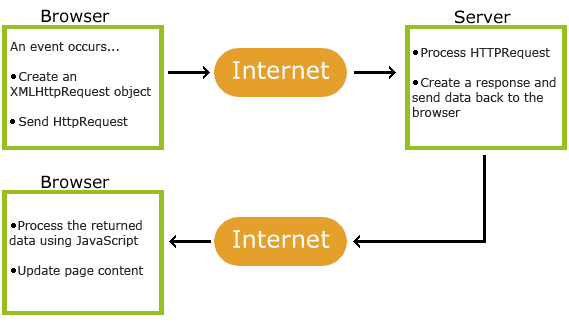
AJAX is Based on Internet Standards
AJAX is based on internet standards, and uses a combination of:- XMLHttpRequest object (to exchange data asynchronously with a server)
- JavaScript/DOM (to display/interact with the information)
- CSS (to style the data)
- XML (often used as the format for transferring data)
Google Suggest
AJAX was made popular in 2005 by Google, with Google Suggest.Google Suggest is using AJAX to create a very dynamic web interface: When you start typing in Google's search box, a JavaScript sends the letters off to a server and the server returns a list of suggestions.
Sunday, 10 July 2011
PHP XML :: SimpleXML
SimpleXML handles the most common XML tasks and leaves the rest for other extensions.
What is SimpleXML?
SimpleXML is new in PHP 5. It is an easy way of getting an element's attributes and text, if you know the XML document's layout.
Compared to DOM or the Expat parser, SimpleXML just takes a few lines of code to read text data from an element.
SimpleXML converts the XML document into an object, like this:
- Elements - Are converted to single attributes of the SimpleXMLElement object. When there's more than one element on one level, they're placed inside an array
- Attributes - Are accessed using associative arrays, where an index corresponds to the attribute name
- Element Data - Text data from elements are converted to strings. If an element has more than one text node, they will be arranged in the order they are found
SimpleXML is fast and easy to use when performing basic tasks like:
- Reading XML files
- Extracting data from XML strings
- Editing text nodes or attributes
However, when dealing with advanced XML, like namespaces, you are better off using the Expat parser or the XML DOM.
Installation
As of PHP 5.0, the SimpleXML functions are part of the PHP core. There is no installation needed to use these functions.
Using SimpleXML
Below is an XML file:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> |
We want to output the element names and data from the XML file above.
Here's what to do:
- Load the XML file
- Get the name of the first element
- Create a loop that will trigger on each child node, using the children() function
- Output the element name and data for each child node
Example
| <?php $xml = simplexml_load_file("test.xml"); echo $xml->getName() . "<br />"; foreach($xml->children() as $child) { echo $child->getName() . ": " . $child . "<br />"; } ?> |
The output of the code above will be:
| note to: Tove from: Jani heading: Reminder body: Don't forget me this weekend! |
PHP XML :: DOM
What is DOM?
The W3C DOM provides a standard set of objects for HTML and XML documents, and a standard interface for accessing and manipulating them.
The W3C DOM is separated into different parts (Core, XML, and HTML) and different levels (DOM Level 1/2/3):
* Core DOM - defines a standard set of objects for any structured document
* XML DOM - defines a standard set of objects for XML documents
* HTML DOM - defines a standard set of objects for HTML documents
The W3C DOM is separated into different parts (Core, XML, and HTML) and different levels (DOM Level 1/2/3):
* Core DOM - defines a standard set of objects for any structured document
* XML DOM - defines a standard set of objects for XML documents
* HTML DOM - defines a standard set of objects for HTML documents
XML Parsing
To read and update - create and manipulate - an XML document, you will need an XML parser.
There are two basic types of XML parsers:
- Tree-based parser: This parser transforms an XML document into a tree structure. It analyzes the whole document, and provides access to the tree elements
- Event-based parser: Views an XML document as a series of events. When a specific event occurs, it calls a function to handle it
The DOM parser is an tree-based parser.
Look at the following XML document fraction:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <from>Jani</from> |
The XML DOM sees the XML above as a tree structure:
- Level 1: XML Document
- Level 2: Root element: <from>
- Level 3: Text element: "Jani"
Installation
The DOM XML parser functions are part of the PHP core. There is no installation needed to use these functions.
An XML File
The XML file below will be used in our example:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> |
Load and Output XML
We want to initialize the XML parser, load the xml, and output it:
Example
| <?php $xmlDoc = new DOMDocument(); $xmlDoc->load("note.xml"); print $xmlDoc->saveXML(); ?> |
The output of the code above will be:
If you select "View source" in the browser window, you will see the following HTML:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> |
The example above creates a DOMDocument-Object and loads the XML from "note.xml" into it.
Then the saveXML() function puts the internal XML document into a string, so we can output it.
Looping through XML
We want to initialize the XML parser, load the XML, and loop through all elements of the <note> element:
Example
| <?php $xmlDoc = new DOMDocument(); $xmlDoc->load("note.xml"); $x = $xmlDoc->documentElement; foreach ($x->childNodes AS $item) { print $item->nodeName . " = " . $item->nodeValue . "<br />"; } ?> |
The output of the code above will be:
| #text = to = Tove #text = from = Jani #text = heading = Reminder #text = body = Don't forget me this weekend! #text = |
In the example above you see that there are empty text nodes between each element.
When XML generates, it often contains white-spaces between the nodes. The XML DOM parser treats these as ordinary elements, and if you are not aware of them, they sometimes cause problems.
PHP XML :: Introduction
The built-in Expat parser makes it possible to process XML documents in PHP.
What is XML?
XML is used to describe data and to focus on what data is. An XML file describes the structure of the data.
In XML, no tags are predefined. You must define your own tags.
What is Expat?
To read and update - create and manipulate - an XML document, you will need an XML parser.
There are two basic types of XML parsers:
- Tree-based parser: This parser transforms an XML document into a tree structure. It analyzes the whole document, and provides access to the tree elements. e.g. the Document Object Model (DOM)
- Event-based parser: Views an XML document as a series of events. When a specific event occurs, it calls a function to handle it
The Expat parser is an event-based parser.
Event-based parsers focus on the content of the XML documents, not their structure. Because of this, event-based parsers can access data faster than tree-based parsers.
Look at the following XML fraction:
| <from>Jani</from> |
An event-based parser reports the XML above as a series of three events:
- Start element: from
- Start CDATA section, value: Jani
- Close element: from
The XML example above contains well-formed XML. However, the example is not valid XML, because there is no Document Type Definition (DTD) associated with it.
However, this makes no difference when using the Expat parser. Expat is a non-validating parser, and ignores any DTDs.
As an event-based, non-validating XML parser, Expat is fast and small, and a perfect match for PHP web applications.
Note: XML documents must be well-formed or Expat will generate an error.
Installation
The XML Expat parser functions are part of the PHP core. There is no installation needed to use these functions.
An XML File
The XML file below will be used in our example:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> |
Initializing the XML Parser
We want to initialize the XML parser in PHP, define some handlers for different XML events, and then parse the XML file.
Example
| <?php //Initialize the XML parser $parser=xml_parser_create(); //Function to use at the start of an element function start($parser,$element_name,$element_attrs) { switch($element_name) { case "NOTE": echo "-- Note --<br />"; break; case "TO": echo "To: "; break; case "FROM": echo "From: "; break; case "HEADING": echo "Heading: "; break; case "BODY": echo "Message: "; } } //Function to use at the end of an element function stop($parser,$element_name) { echo "<br />"; } //Function to use when finding character data function char($parser,$data) { echo $data; } //Specify element handler xml_set_element_handler($parser,"start","stop"); //Specify data handler xml_set_character_data_handler($parser,"char"); //Open XML file $fp=fopen("test.xml","r"); //Read data while ($data=fread($fp,4096)) { xml_parse($parser,$data,feof($fp)) or die (sprintf("XML Error: %s at line %d", xml_error_string(xml_get_error_code($parser)), xml_get_current_line_number($parser))); } //Free the XML parser xml_parser_free($parser); ?> |
The output of the code above will be:
| -- Note -- To: Tove From: Jani Heading: Reminder Message: Don't forget me this weekend! |
How it works:
- Initialize the XML parser with the xml_parser_create() function
- Create functions to use with the different event handlers
- Add the xml_set_element_handler() function to specify which function will be executed when the parser encounters the opening and closing tags
- Add the xml_set_character_data_handler() function to specify which function will execute when the parser encounters character data
- Parse the file "test.xml" with the xml_parse() function
- In case of an error, add xml_error_string() function to convert an XML error to a textual description
- Call the xml_parser_free() function to release the memory allocated with the xml_parser_create() function
Labels:
CDATA,
Document Type Definition,
DTD,
Expat,
MySQL,
parser,
PHP,
XML,
XML Parser,
xml_parser_create
PHP MySQL :: ODBC Connection
ODBC is an Application Programming Interface (API) that allows you to connect to a data source (e.g. an MS Access database).
Create an ODBC Connection
With an ODBC connection, you can connect to any database, on any computer in your network, as long as an ODBC connection is available.
Here is how to create an ODBC connection to a MS Access Database:
- Open the Administrative Tools icon in your Control Panel.
- Double-click on the Data Sources (ODBC) icon inside.
- Choose the System DSN tab.
- Click on Add in the System DSN tab.
- Select the Microsoft Access Driver. Click Finish.
- In the next screen, click Select to locate the database.
- Give the database a Data Source Name (DSN).
- Click OK.
Note that this configuration has to be done on the computer where your web site is located. If you are running Internet Information Server (IIS) on your own computer, the instructions above will work, but if your web site is located on a remote server, you have to have physical access to that server, or ask your web host to to set up a DSN for you to use.
Connecting to an ODBC
The odbc_connect() function is used to connect to an ODBC data source. The function takes four parameters: the data source name, username, password, and an optional cursor type.
The odbc_exec() function is used to execute an SQL statement.
Example
The following example creates a connection to a DSN called northwind, with no username and no password. It then creates an SQL and executes it:
| $conn=odbc_connect('northwind','',''); $sql="SELECT * FROM customers"; $rs=odbc_exec($conn,$sql); |
Retrieving Records
The odbc_fetch_row() function is used to return records from the result-set. This function returns true if it is able to return rows, otherwise false.
The function takes two parameters: the ODBC result identifier and an optional row number:
| odbc_fetch_row($rs) |
Retrieving Fields from a Record
The odbc_result() function is used to read fields from a record. This function takes two parameters: the ODBC result identifier and a field number or name.
The code line below returns the value of the first field from the record:
| $compname=odbc_result($rs,1); |
The code line below returns the value of a field called "CompanyName":
| $compname=odbc_result($rs,"CompanyName"); |
Closing an ODBC Connection
The odbc_close() function is used to close an ODBC connection.
| odbc_close($conn); |
An ODBC Example
The following example shows how to first create a database connection, then a result-set, and then display the data in an HTML table.
| <html> <body> <?php $conn=odbc_connect('northwind','',''); if (!$conn) {exit("Connection Failed: " . $conn);} $sql="SELECT * FROM customers"; $rs=odbc_exec($conn,$sql); if (!$rs) {exit("Error in SQL");} echo "<table><tr>"; echo "<th>Companyname</th>"; echo "<th>Contactname</th></tr>"; while (odbc_fetch_row($rs)) { $compname=odbc_result($rs,"CompanyName"); $conname=odbc_result($rs,"ContactName"); echo "<tr><td>$compname</td>"; echo "<td>$conname</td></tr>"; } odbc_close($conn); echo "</table>"; ?> </body> </html> |
PHP MySQL :: Delete Data In a Database
The DELETE statement is used to delete records in a table.
Delete Data In a Database
The DELETE FROM statement is used to delete records from a database table.
Syntax
| DELETE FROM table_name WHERE some_column = some_value |
Note: Notice the WHERE clause in the DELETE syntax. The WHERE clause specifies which record or records that should be deleted. If you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be deleted!
To get PHP to execute the statement above we must use the mysql_query() function. This function is used to send a query or command to a MySQL connection.
Example
Look at the following "Persons" table:
| FirstName | LastName | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Peter | Griffin | 35 |
| Glenn | Quagmire | 33 |
The following example deletes all the records in the "Persons" table where LastName='Griffin':
| <?php $con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123"); if (!$con) { die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error()); } mysql_select_db("my_db", $con); mysql_query("DELETE FROM Persons WHERE LastName='Griffin'"); mysql_close($con); ?> |
After the deletion, the table will look like this:
| FirstName | LastName | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Glenn | Quagmire | 33 |
Labels:
Database,
DELETE,
FROM,
MySQL,
mysql_connect,
mysql_query,
PHP,
SELECT,
WHERE clause
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)